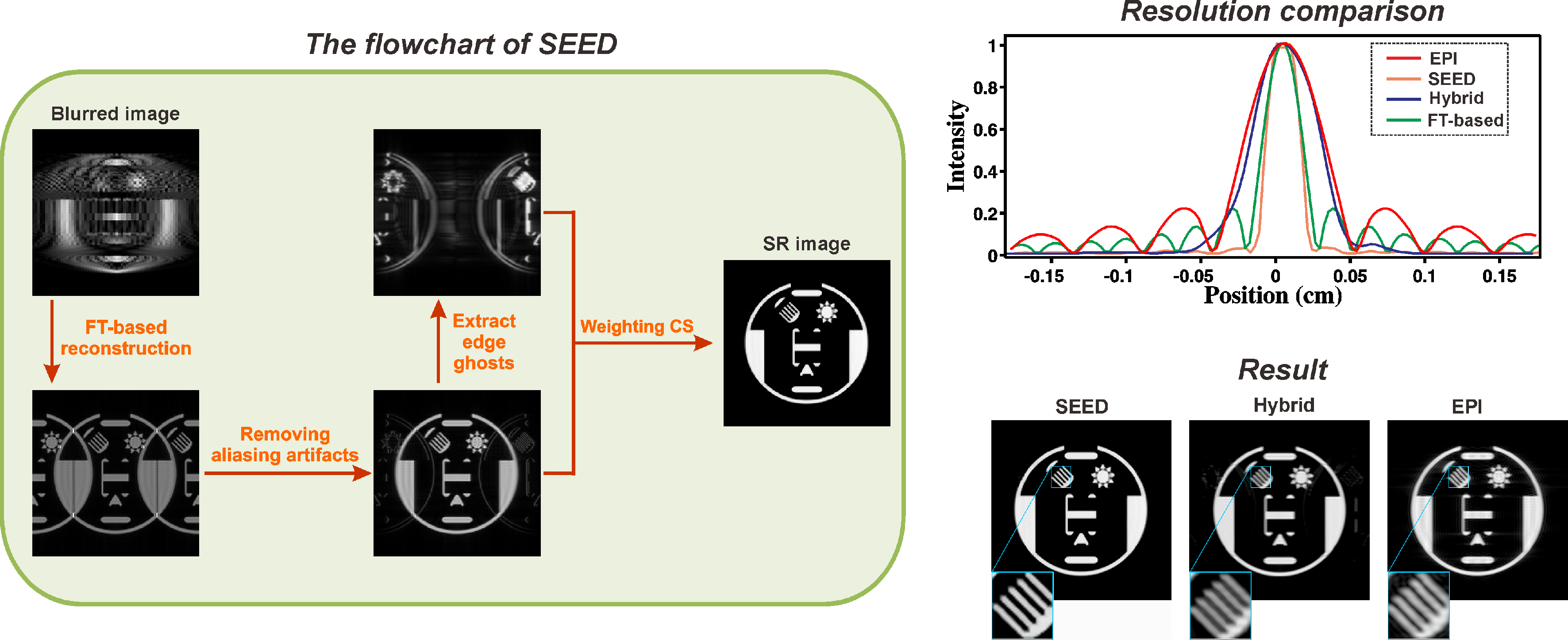
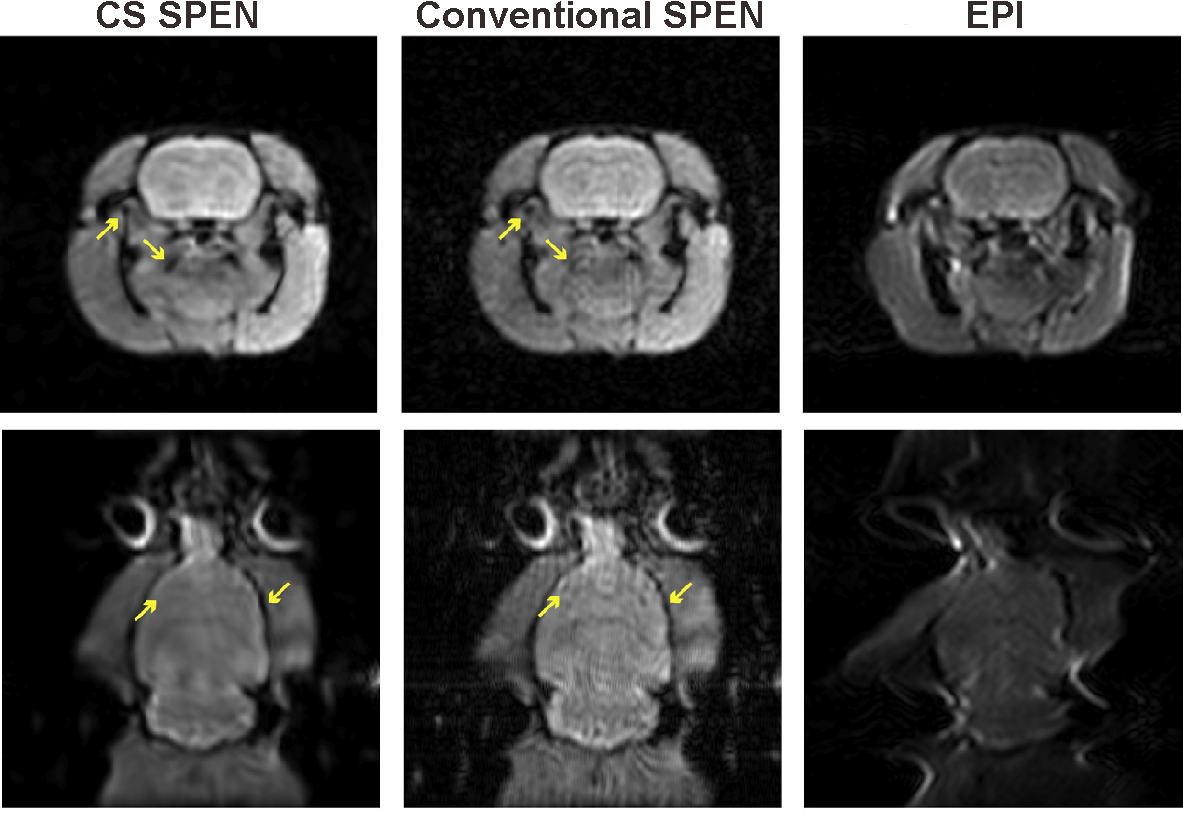
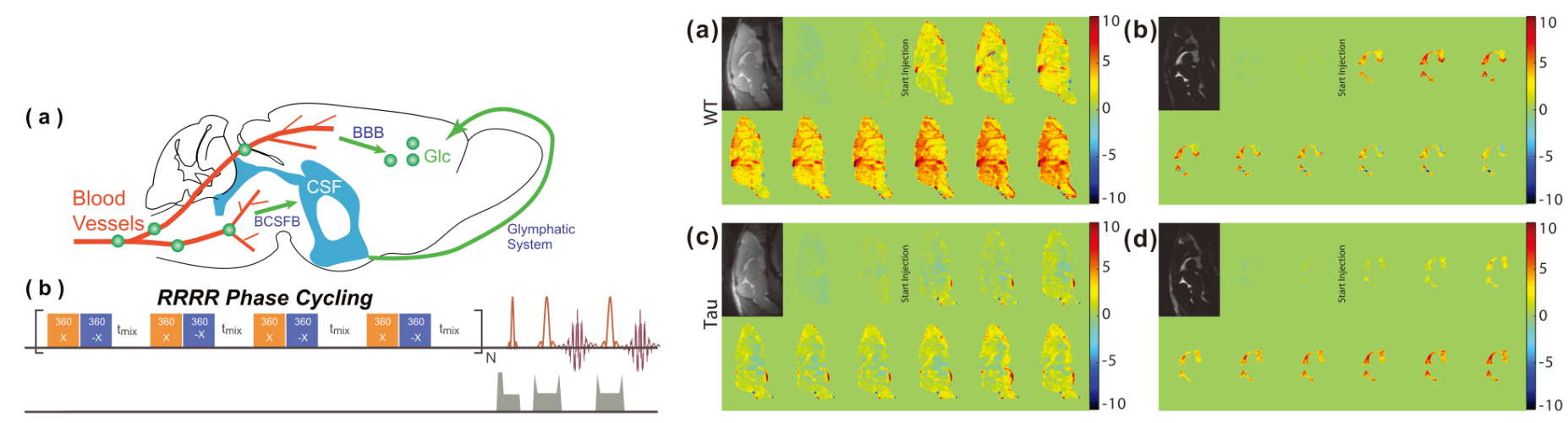
D-Glucose uptake and clearance in the tauopathy Alzheimer’s disease mouse brain detected by on-resonance variable delay multiple pulse MRI
Published in Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 2020
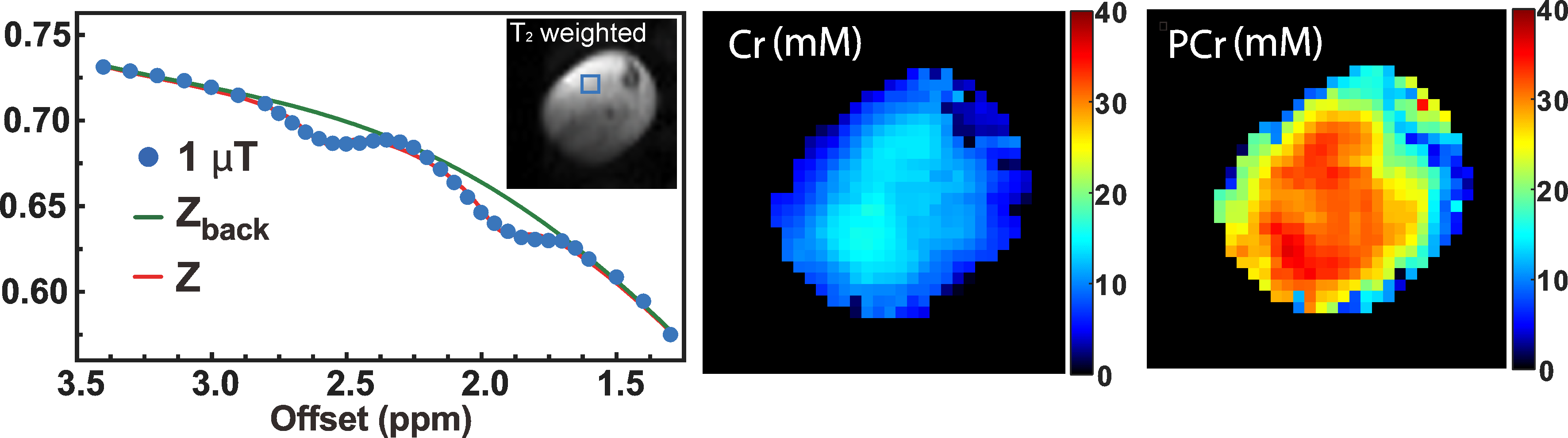
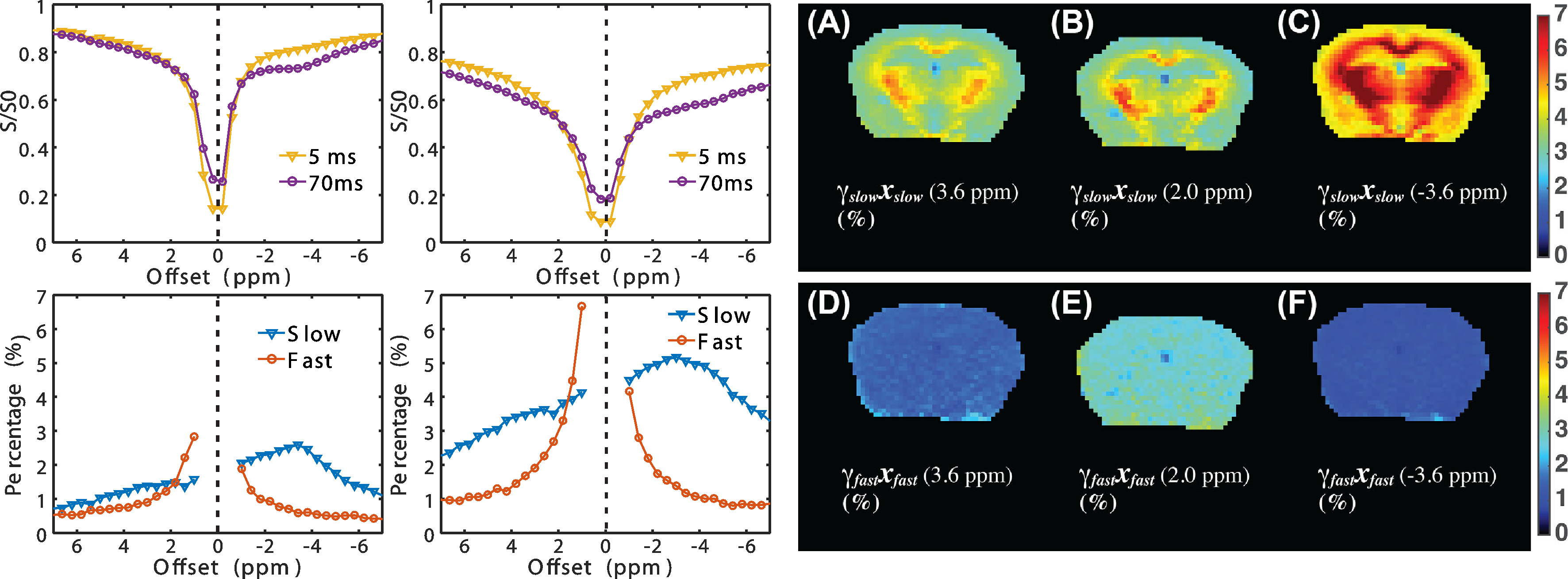
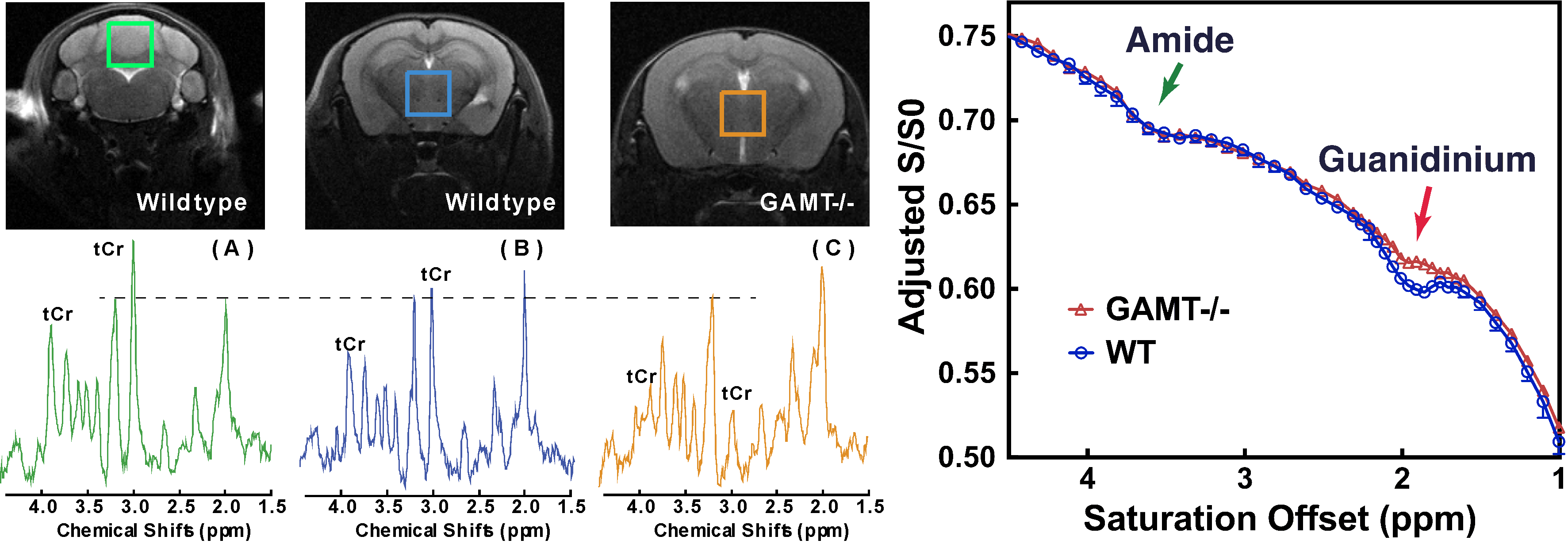
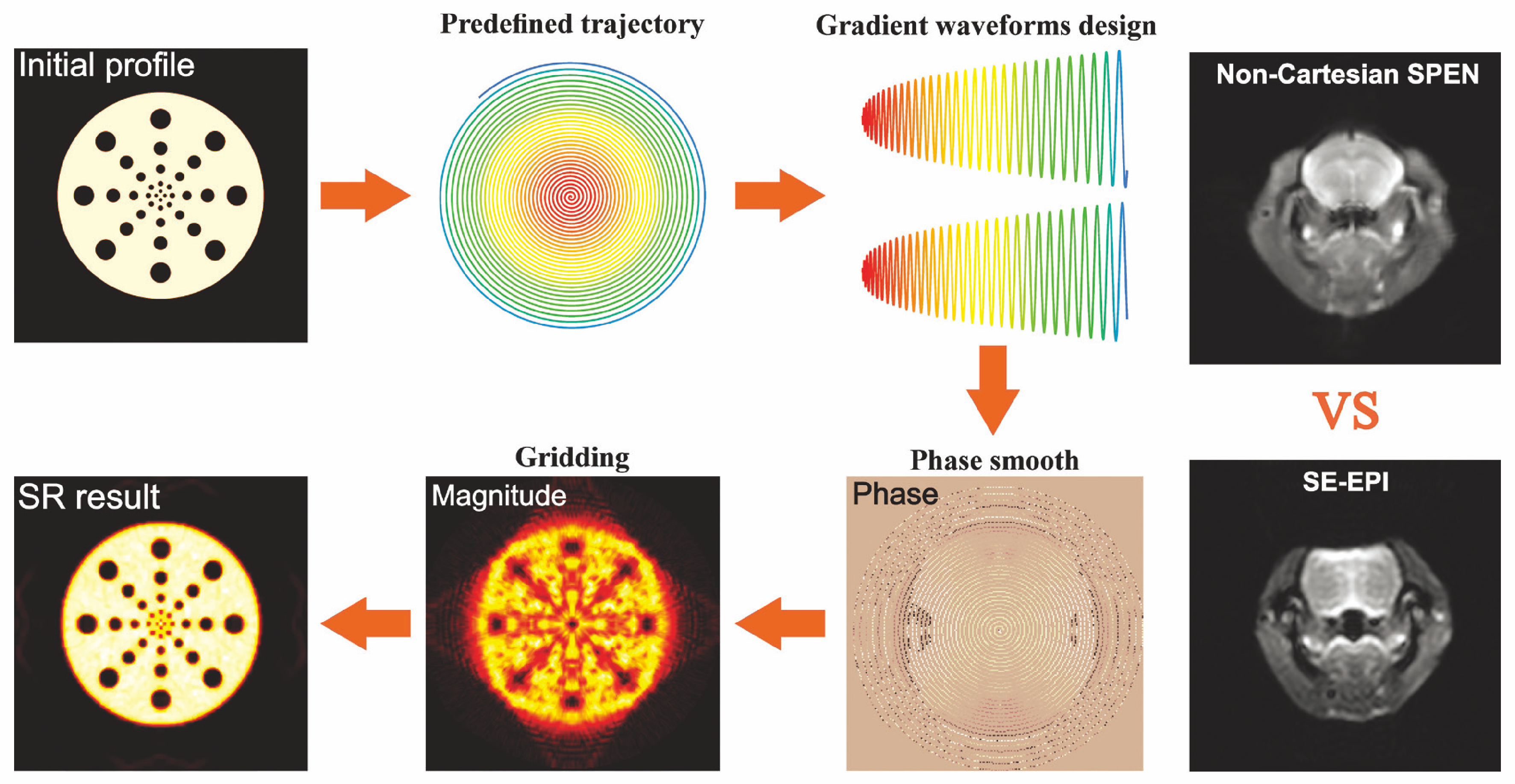
Functioning of the glucose transporter and glymphatic systems in the tauopathy AD mouse brain studied by onVDMP MRI and D-glucose infusion
Recommended citation: Chen L, Wei Z, Chan KWY, Li Y, Suchal K, Bi S, Huang J, Xu X, Wong PC, Lu H, van Zijl PCM, Li T, Xu J. D-Glucose uptake and clearance in the tauopathy Alzheimer's disease mouse brain detected by on-resonance variable delay multiple pulse MRI. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 2020; https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X20941264